EOxHub uses Argo Workflows as its workflow orchestration tool, providing a solution for defining and executing multi-step processing pipelines where each step runs in its own container.
This enables scalable and repeatable execution of applications, supporting both simple tasks and complex, long-running jobs.
A web-based workflow editor is included, offering operators an intuitive interface to design, manage, and visualize workflows.
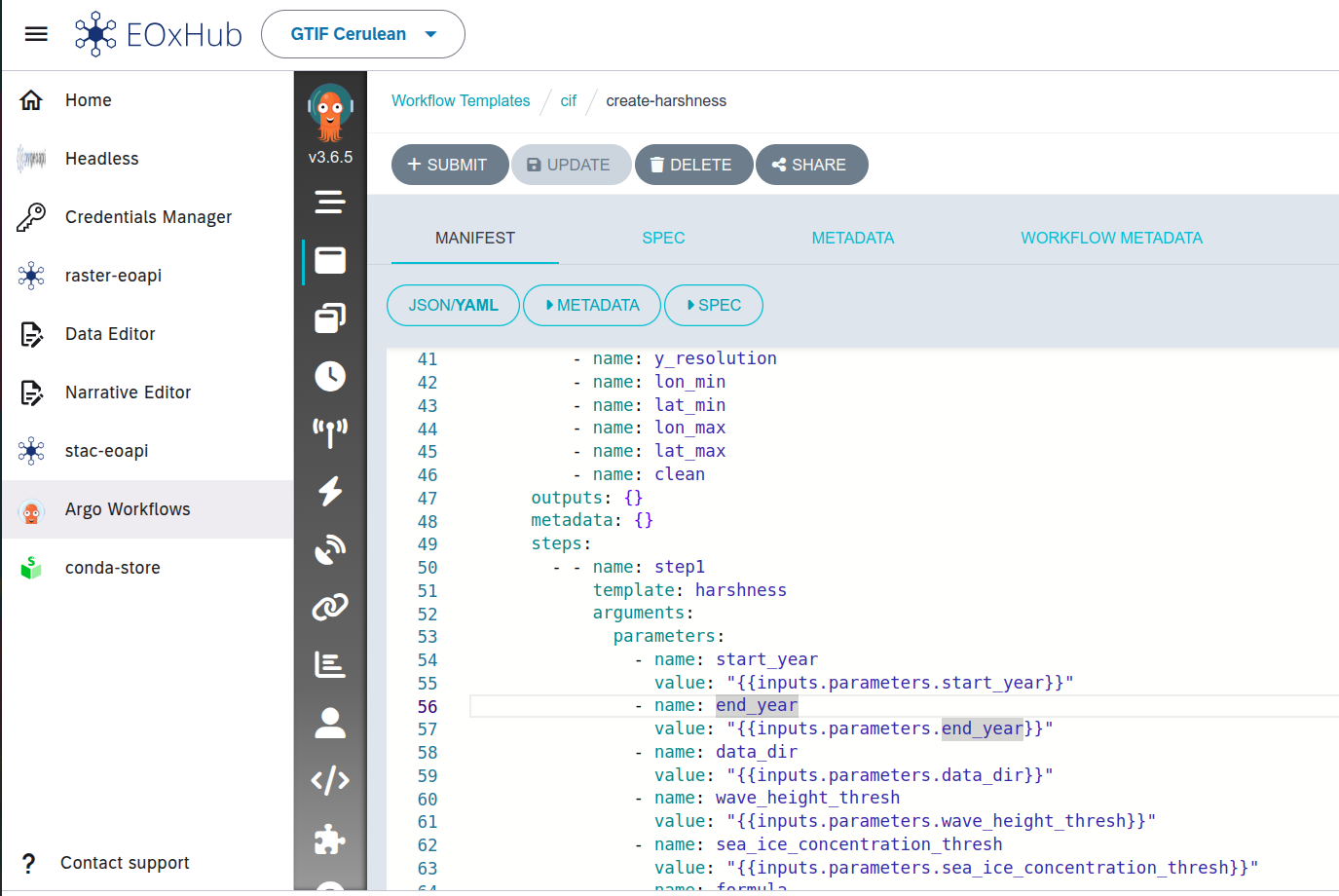
Figure 1:Argo Workflow Templates input mapping in web editor
Applications are published in the platform as Docker images, which can be versioned and reused across different workflows. Argo’s native support for dynamic parameter passing and conditional logic enables the creation of modular pipelines.
In addition to on-demand execution, workflows can be scheduled for automated, repeated execution using cron triggers.
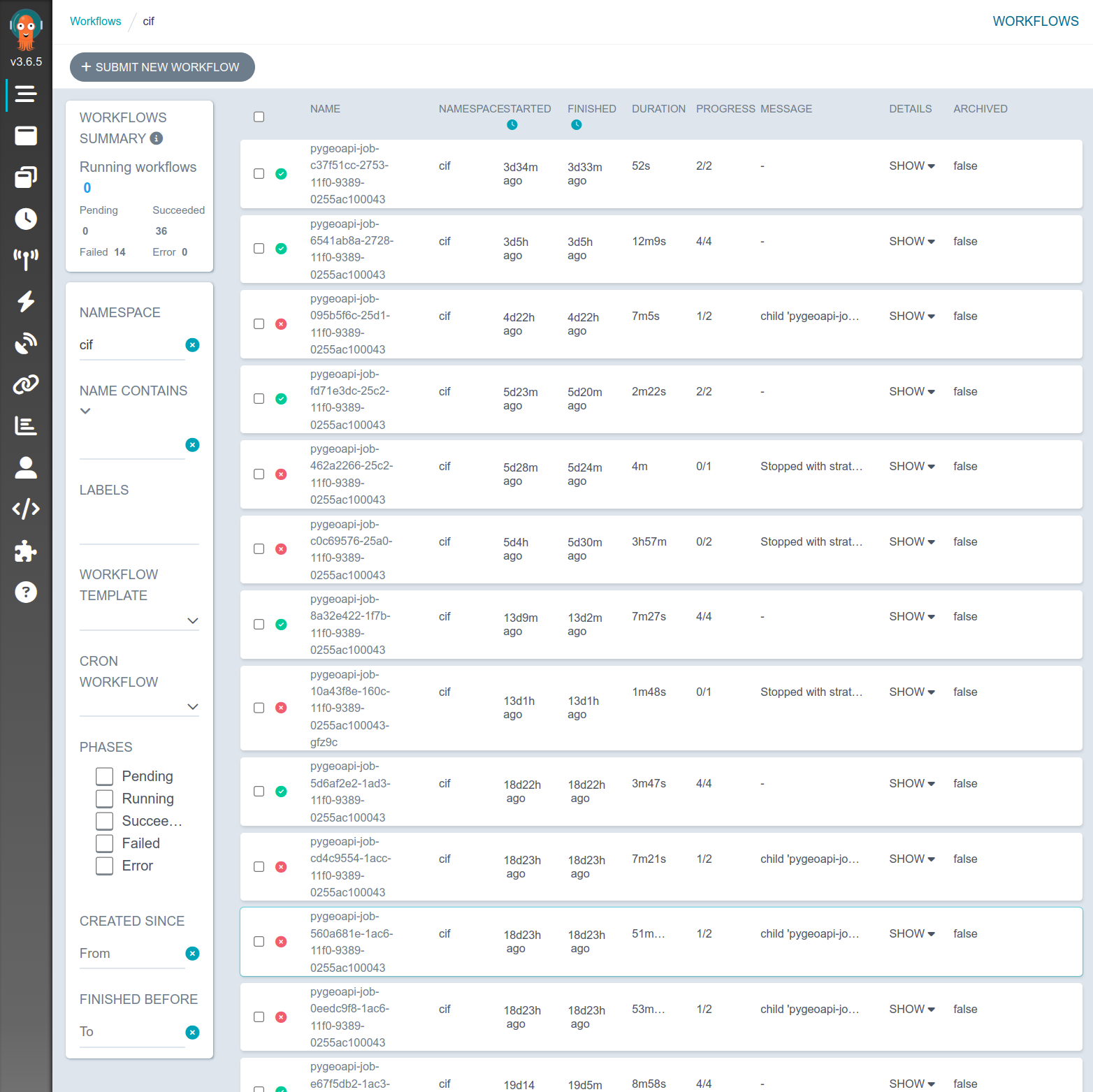
Figure 2:Argo Workflow server
Argo Workflows also provides detailed logs for all executions, enabling workspace administrator to monitor behavior, trace failures, and debug issues.
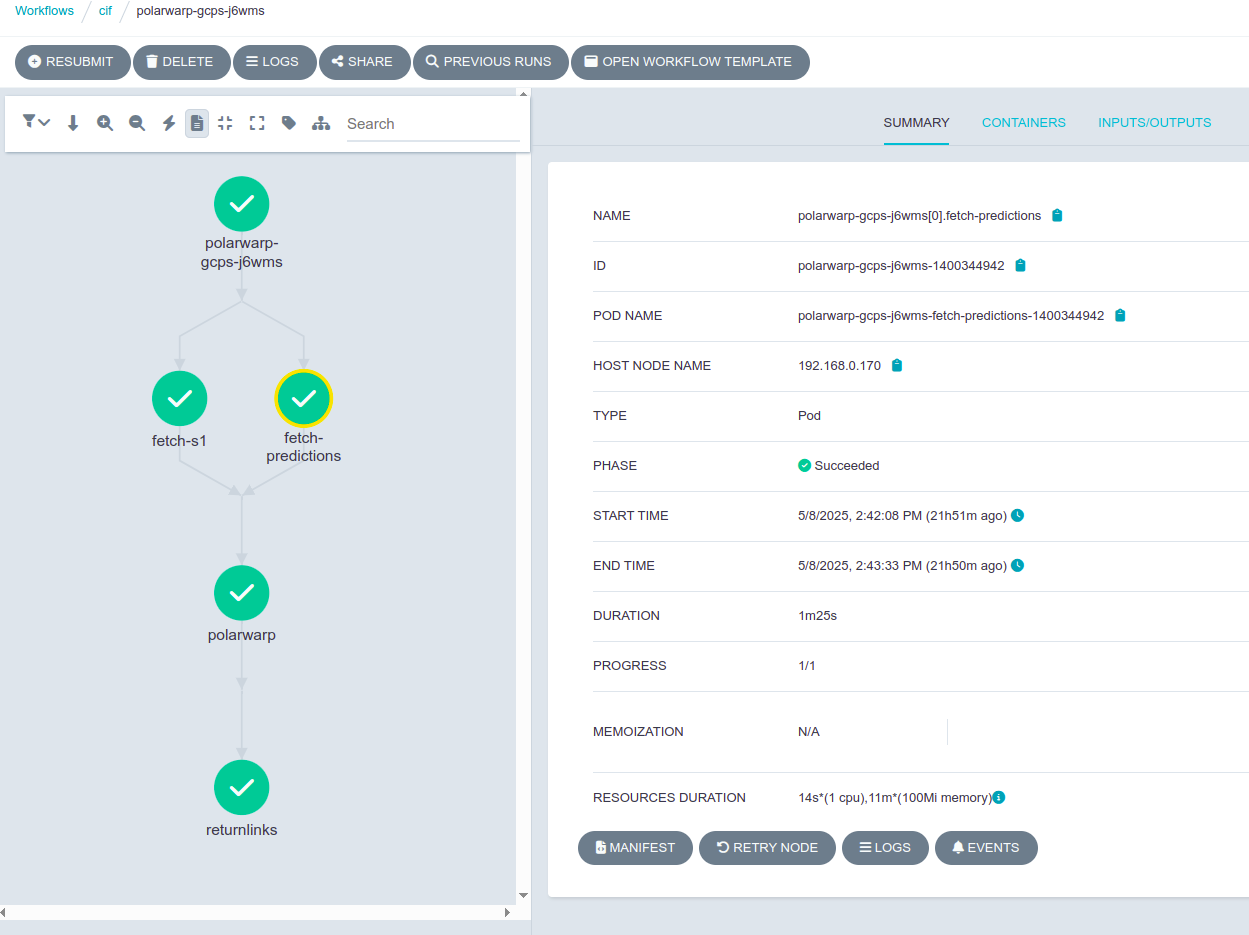
Figure 3:Argo Workflows details of a finished workflow with details of a step
Sample templates will become available in the tutorial section once possible
Capability requirements for integration¶
Docker image/capability requirements for integration are described on the separate page
Argo workflow steps¶
Each workflow includes usually following types of steps:
Workflow input parameters and configuration of secrets (e.g., API tokens) as environment variables.
Definition of processing steps, such as data retrieval, transformation, analysis, and result management.
Inter-step communication via shared persistent storage for handling intermediate data between containers.
Data retrieval¶
Examples of data retrieval approaches include:
The container directly handles the download or access to external or internal data sources.
Data is passed from a previous workflow step.
Data already exists in the shared storage. It may have been placed there by scheduled (e.g. daily) Argo workflows or manually.
Result management¶
Result management of the workflow may include:
Writing output files to client-controlled storage buckets or centralized handover locations.
Returning signed URLs or object storage paths as outputs for M2M scenarios. These can be persisted and exposed through
pygeoapiinterfaces, e.g., as utilized as a structured JSON as utilized byeodashprocessing widget.Automatic registration of outputs along with necessary metadata as STAC Items in a workspace STAC catalog or a STAC API.
Metrics¶
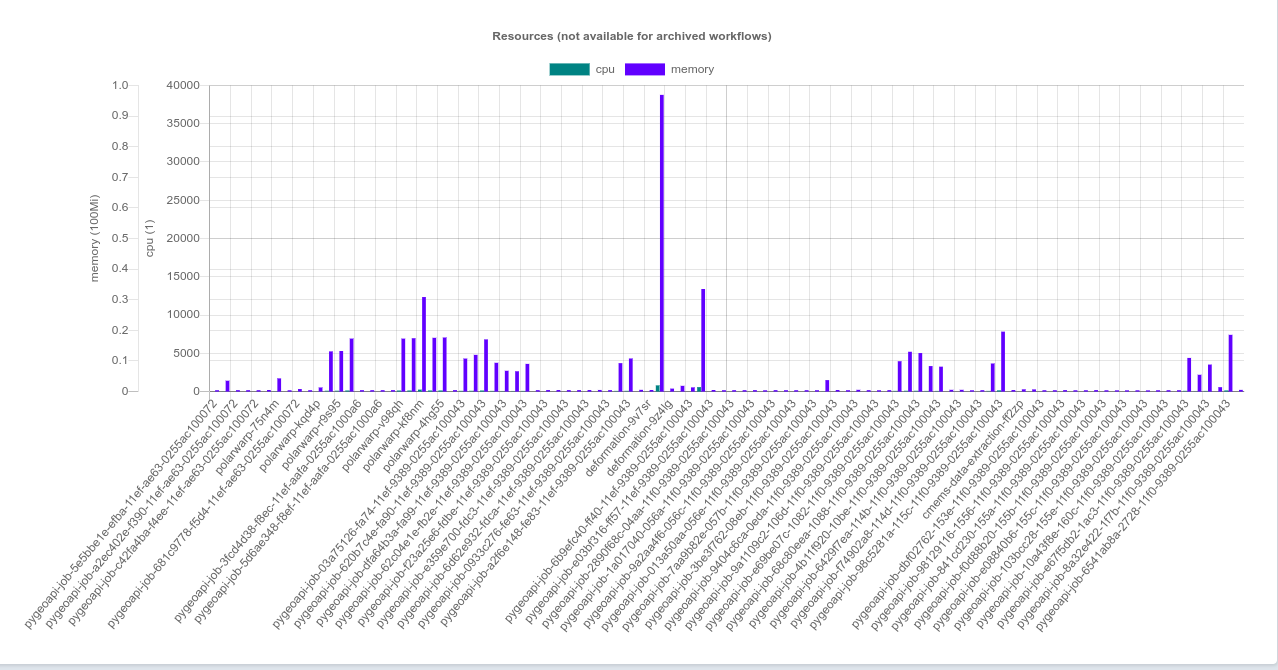
Figure 4:Argo Workflow Server built in resource usage metrics